Of recent days, Windows 10 has shown relentless disappointments to their users. There have been problems with various updates to the systems. Many business computers may have become unusable because the updates cause freezing of computers among other problems. Even in the most recent May 2019 update, people are still complaining about several issues.
For people who do not rely on native Windows applications, Linux is a free Operating System you can try on your machine. Even without the update problems, many people have been using Linux for various reasons from the past. And among the most common Linux distros for PCs, Ubuntu is second, after Linux Mint.
People who use Ubuntu rely on it because it comes with most drivers and software necessary to run most hardware in the market out of the box. It is also easy to manage and update the software on Ubuntu and its derivatives. If you have not tried it yet, learn why you need to and how to install Ubuntu on your Windows 10 PC.
About Boosting Ubuntu Performance
If you are new to Ubuntu, you will notice that the desktop is not as fast as Windows. If you are, especially, playing games or videos on your PC or laptop while browsing a few tabs on the web, the system may show signs of lagging. This is true when you have an old PC that has less powerful resources compared to the modern and sophisticated systems.
In this post, you will learn the steps you need to take to make your computer run faster on your laptop. You do not have to execute every tip. Do a few checks on your laptop as necessary to improve the performance without limiting the features, functionality, and appearance of your system.
Remember that because the hardware varies from one computer to another, your solution to the slowness of the laptop may not work for another person. So, you will have to find out what works best for you.
Here are the best tips on how to speed up ubuntu
1. Reboot the Laptop
This one may seem pretty basic and inefficient. But wait. Sometimes we run the laptops for many days without shutting them down. For instance, there are times I did not shut mine for many weeks. I play games, do some jobs online, watch videos on YouTube or on the local storage, and use it as a music player in my house.
When using the laptop for many hours, we tend to overwork it. The performance may start to go down slowly. The system memory cache and browser caches expire with time, and you will have difficulties loading apps, web pages, and reading filesystem contents.
A reboot will help to clear the memory so that you can start from a fresh memory. If your laptop overheats after hours or days of usage, it is ideal to shut it down completely. Let it cool before you boot Ubuntu again. This helps to ease the CPU so that the system can run smoothly.
Before you reboot your Ubuntu laptop, ensure that you have saved all the files you have open and close any running GUI programs to avoid losing data. In case you are running a program on the terminal that is accessing data on the hard drive, terminate the process as well.
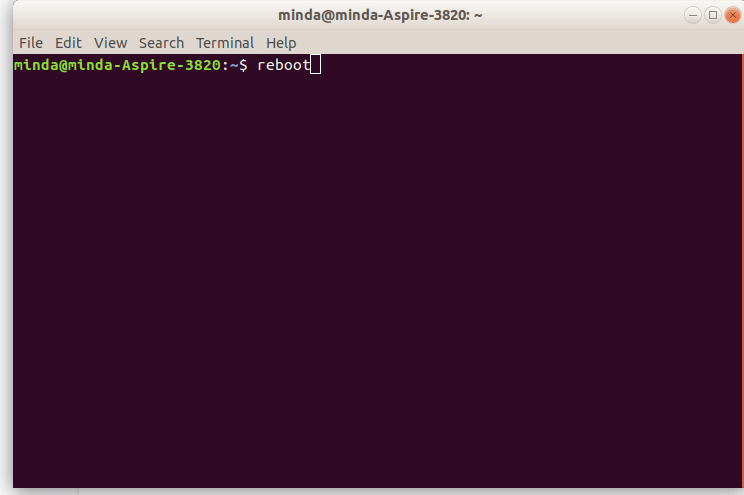
Sometimes the GUI desktop may be too laggy to access the menu items. You can shutdown or reboot your laptop from the terminal as well. CTRL+ALT+T opens the terminal. The command to enter on the terminal emulator to restart the machine is reboot while shutdown or poweroff will turn the laptop off.
2. Upgrade Your PC RAM

If you are running an oil system like computers designed for Windows 7 or earlier versions, then you may be using low RAM on the computer. For instance, my laptop (It dates back to 2009 when SATA was a new technology and Windows 7 was a new product in the market.) came with a RAM of 2GB and the system was running fine with Windows 7.
Installing Ubuntu on my PC was a milestone in my dreams. But then I discovered that the system used to lag a lot. With only three tabs open on Firefox, the laptop could stop loading and the browser freeze (showing Firefox is not responding). Every time I had to kill the process from the terminal to release the memory and restart Firefox or run another app.
A simple Google search hinted that I may be using a desktop environment that consumes too much RAM space. And that was true. Ubuntu comes with two or three DEs and Unity is the heaviest of all.
But the way I love the Unity dash, I was not ready to remove it. I had to upgrade the RAM. I added a 2 GB RAM (My machine has two slots for RAM) and my problem vanished.
But the more recent Windows 10 PCs come with 4 GB RAM or more. Conventionally, you can expect that to be sufficient to run your OS smoothly. But again it is not always true. If you are not willing to upgrade your laptop RAM, you may want to take another route.
3. Create Swap Space on Your HDD
It is not enough to increase your computer RAM for Ubuntu to run smoothly. Swap space is necessary to help relieve the RAM so that you can run more programs without freezing your system. Swap is a special filesystem that Linux uses to write temporary data on the hard disk drive while computing.
Unlike windows that creates its own Swap in a .sys file on drive C:, Swap on Ubuntu Linux is a fixed space that you create as a partition. When booting, the OS will find the Swap and mount it automatically.
You cannot open a Swap partition to view files, but the OS uses it to write the data it uses to remember the programs and tasks that you are running on the PC.
If you forgot (or ignored) to create the Swap during the installation process, you can create it manually from your Ubuntu desktop. Here are the steps to create Swap space on Ubuntu.
Install GParted and Run It
Gparted, the graphical partition editor, is the only tool you need for this part. Ensure that you have an active internet connection and press CTRL+ALT+T simultaneously to open the Terminal emulator.
Type sudo apt update on your terminal and press the “ENTER” key to update the software sources.
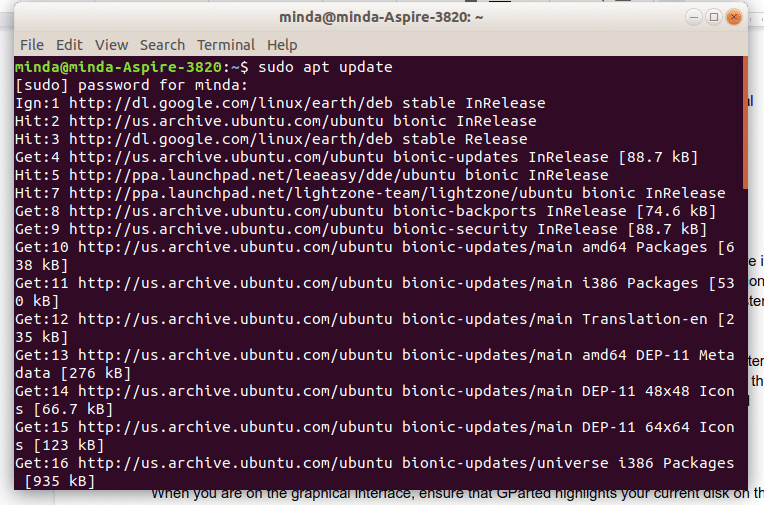
Once the system has updated the sources, type
sudo apt install gparted
The command will install the graphical application (GParted) you need alongside the software it requires to perform the task, libparted (the partition editor library) and the text mode application parted. The graphical interface makes it easy to manipulate the drives without having to master and risk with text commands on the terminal.
To run GParted, you can type the gparted command on the Terminal. You do not need to enter the superuser mode in Terminal. When it is loading, it will ask you for your password so that the application can run administrative tasks (editing the system drives). You can also search and find GParted from the dash and click on the icon to launch the program.
Create the Required Swap Space
When you are on the graphical interface, ensure that GParted highlights your current disk on the editor. In most cases, this will be /dev/sda. But you can identify your disk with the size (in GiB). If you are unsure, ensure you have disconnected all external drives and refresh the disks.
I will assume that you are using the entire space on your HDD. You can create space for Swap by shrinking a partition Remember that when logged in to Ubuntu, you cannot shrink the partition you installed the OS.
You have to shrink one of the other partitions. In case you only have Ubuntu on the laptop, you will need to boot a live USB or DVD to create a partition on your HDD.
The ability to create a partition also depends on whether you are using a GPT or MBR type of filesystem partitioning scheme. Most old systems with only BIOS have MBR as their partition schemes (unless you have changed this with your partition editor, like GParted). Recent hardware come with GPT.
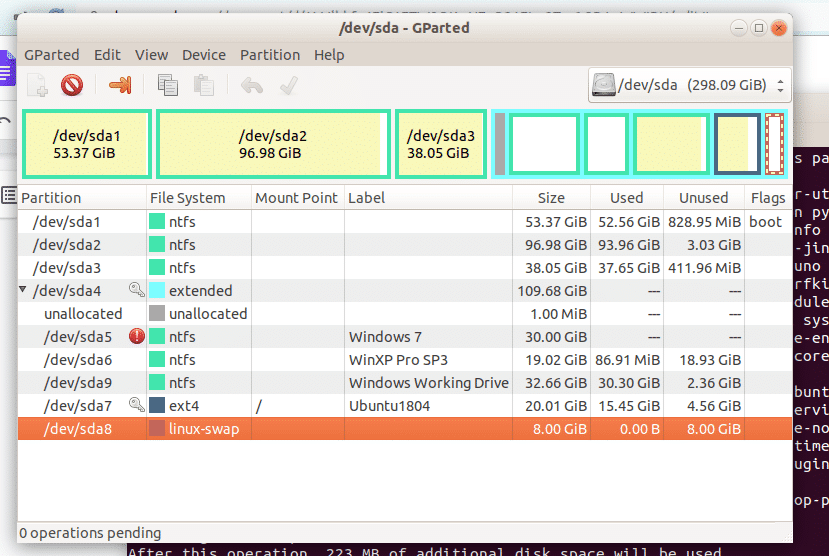
The difference is that MBR only allows up to four primary partitions, and if you need more, you should create a secondary partition and add the rest under it as logical partitions. On GPT, you can create as many partitions on your disk as you need.
When creating a Swap space on your HDD, you should ensure it is twice the size of your installed RAM. If you have a 4GB RAM, then the Swap needs to be 8GB. And you also have to format it as linux-swap.
Whenever you boot the Ubuntu (and all other Linux OS), it will utilize the Swap space to relieve the RAM to ensure your laptop runs smoothly.
4. Ensure Your System is Up to Date
Outdated system software can lag your computer. You need more recent software with security fixes and updates to run your laptop smoothly. You also need to ensure that you run an updated Ubuntu version. But I recommend an LTS release to receive updates for a longer period. The latest LTS is 18.04.
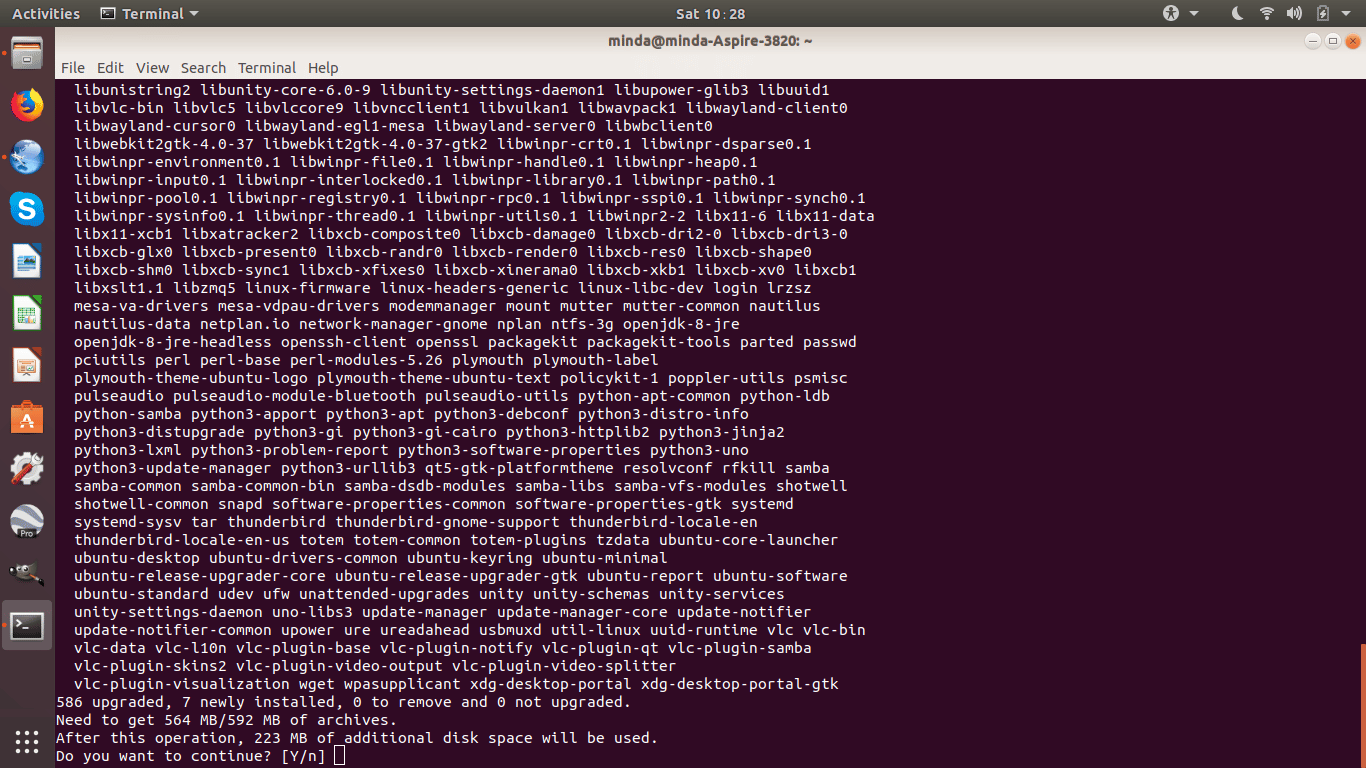
To update your system software, open the terminal and run
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
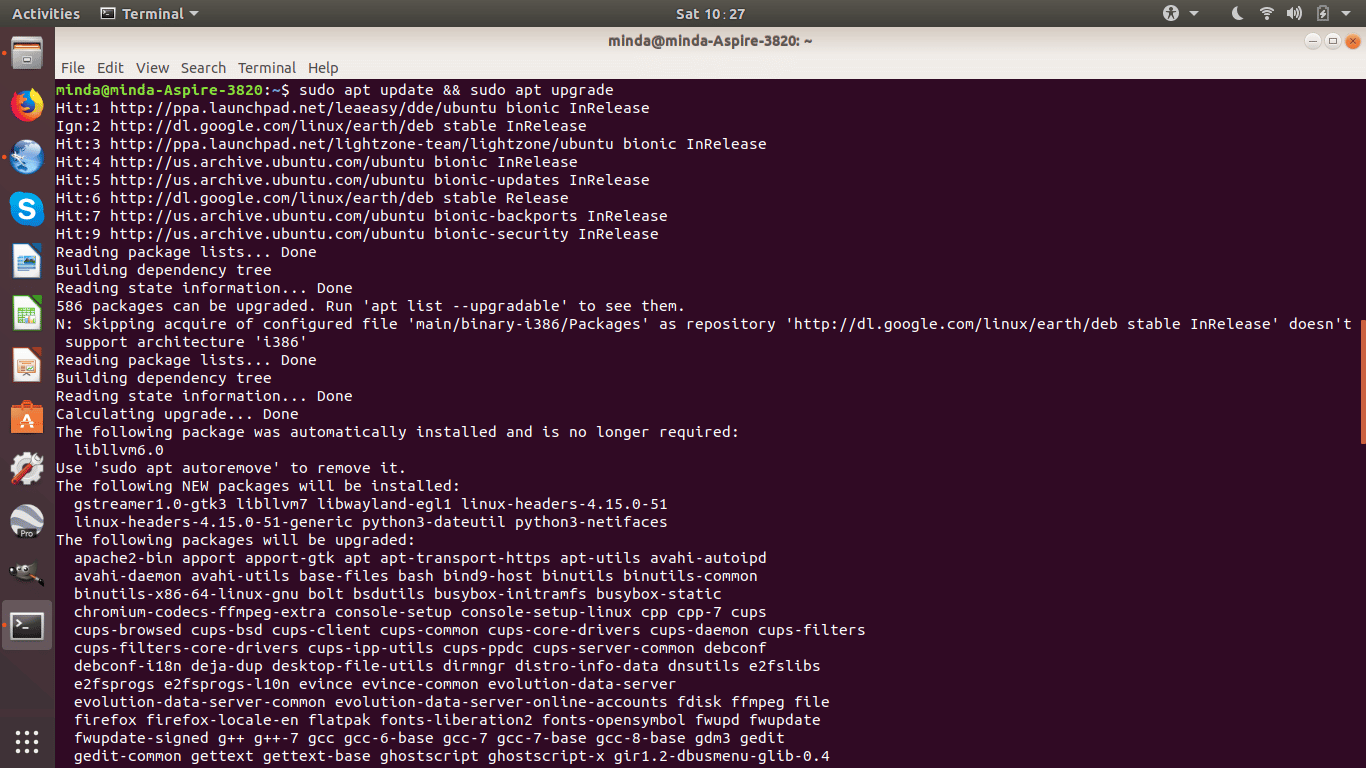
Your computer will update the software sources and install the latest software releases to ensure your computer is secure and stable. In case you get the confirmation prompt, type “Y” to give your consent to update the software.
5. Keep an Eye on the Resource-Hungry Apps
Some applications use the RAM and the processor to the extent they cause the system to crash or hang. Some of the apps can cause overheating by overworking the CPU. You need to monitor the usage on the system and identify the culprits that are slowing down your computer. Kill any unnecessary processes that are overworking your laptop.
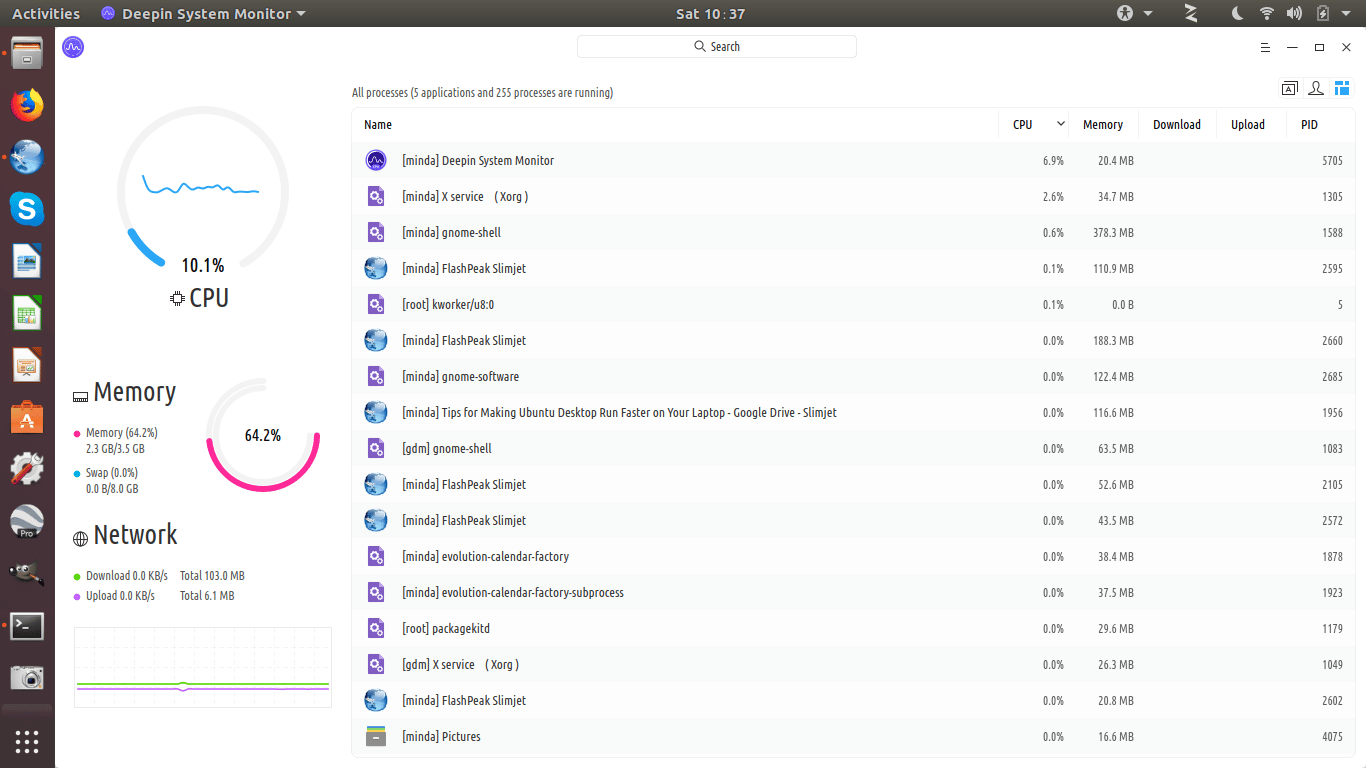
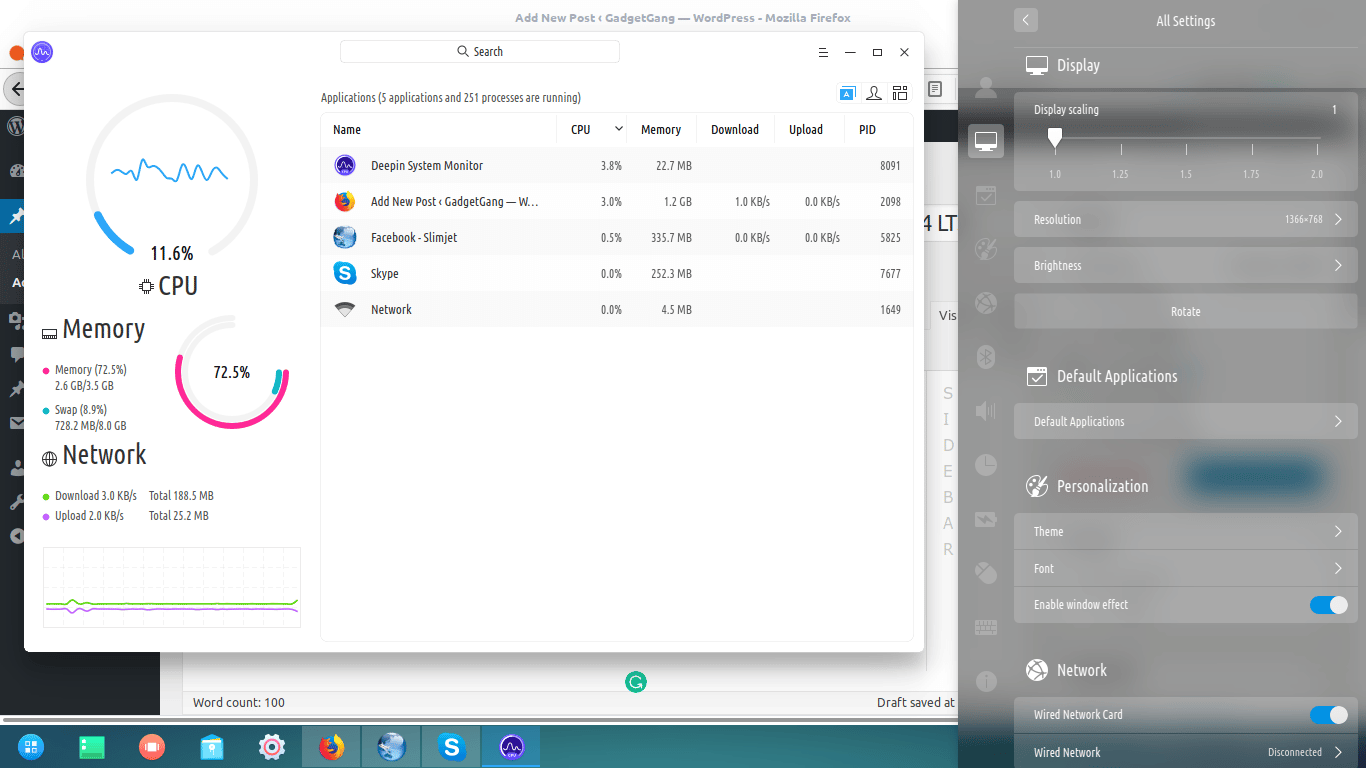
The easiest way to keep an eye on the apps and processes on your Ubuntu laptop is to install the Deepin Desktop Environment on Ubuntu and use its in-built Deepin System Monitor to watch resource usage. You can install alternatives that do not overwork the CPU.
6. Update System from Nearest Mirrors
Something worthy to note about Ubuntu is that it has mirrors all around the world where you can access the updates for your system software. There are many countries that have internet connectivity problems and the speeds are always slow. This slow connection can hinder you from getting the updates you need within the desirable timespan.
You will need to change your software sources to reflect your current or nearest location so that you can get the updates faster. Open the “Software and Updates” app from the system menu (search if you are using the Ubuntu Unity.
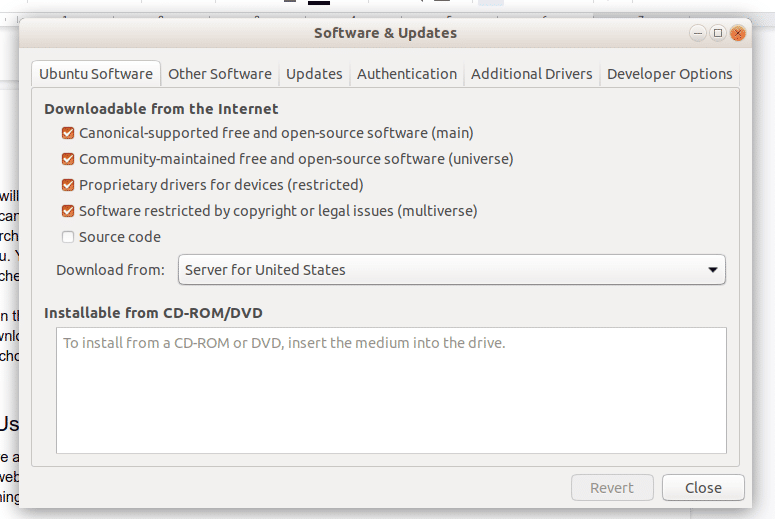
GNOME users can also search from the “activities” menu. You can also show applications by clicking on the 9-dot square at the bottom of the launcher.
When the software updates app launches, click the “Ubuntu Software” tab. Then under the “Download from” menu, choose “Other” and choose the location nearest to you. But I realized that choosing the US as my software source makes the download faster and without errors for me.
7. Use Preload to Launch Apps You Use Often
There are various programs we use more often on our systems than others. For example, I use the web browser every day, and there is no single day my computer will be running without opening Google Chrome to check some updates, do research, or post an article.
In computing, “preloading” is the practice of keeping data in the system memory instead of the local hard disk. We will use a daemon called preload to make the laptop run faster when using Ubuntu (or any other Linux OS).
The daemon will monitor your system for the files you fetch mostly when running your favorite applications and save the data in memory. This makes it faster to open the programs you need.
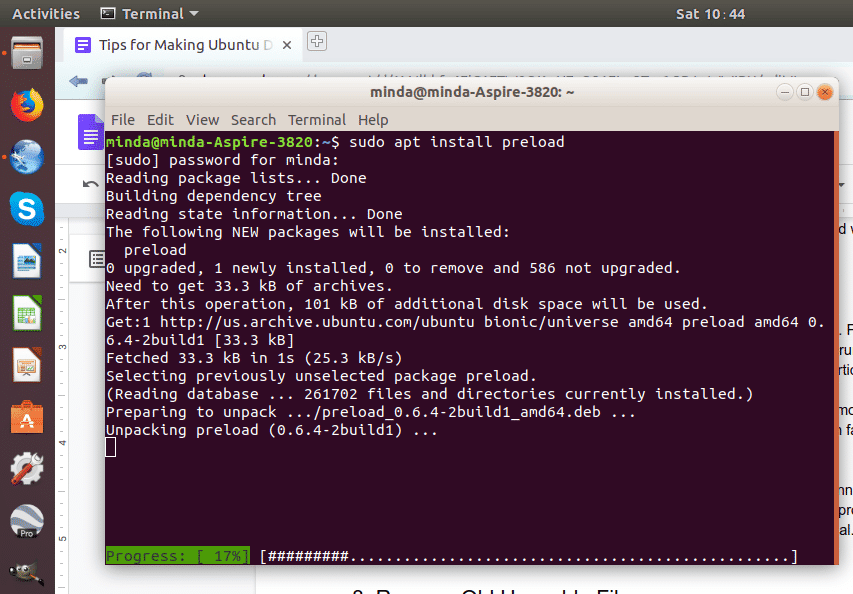
To install preload on your system, run sudo apt install preload on the terminal. When you reboot, the daemon will run in the background to make your computing faster.
8. Remove Old Unusable Files
You do not have to fumble around trying to find what system files you do not need on your system. Every time we install and uninstall apps on the laptop, there are cache files and residuals that remain behind that fill up some disk space. Some unnecessary software also do remain behind as part of the installations you may have done earlier.
To make your computer run faster, you should clean the system periodically to remove any unnecessary junk. There are two commands you will need for this step. Open your terminal and paste these, hitting enter after each.
sudo apt autoclean
sudo apt autoremove --purge
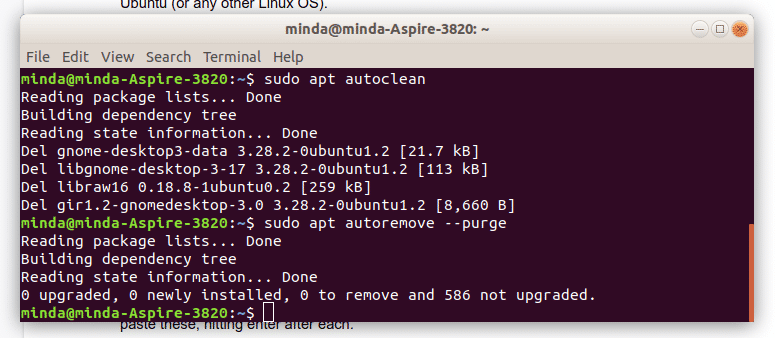
The –purge flag on the second line clears any configurations that might have been saved together with the dependencies installed when managing the software on your computer. Read here to understand why autoclean is necessary instead of clean.
9. Get a New Hard Disk
Over time, as we use our computers, the HDD “wears out” as the system reads and writes files to and fro every time. Repeated reading and writing of data make the drives “tired” and you can start encountering input and output errors. This can tremendously affect the performance of your system.

Overheating is another culprit that damages the hard disks we use in our computers. The rise in temperatures can damage the hard disk and it lowers its durability. In most cases, you will see that your system shuts down without warning when it overheats. The reason it does this is to save your system from corruption and your disks from failure.
If your hard disk starts to slow down the writing speed, or it takes some time before programs respond, it means the disks have started failing. You should back up your data as soon as possible. Then get a new hard disk to install Ubuntu and transfer your files.
A better investment option is to get an SSD. Solid State Drives use flash memory like the USB thumb drives. The writing on SSD is much faster compared to the magnetic writing mechanism in HDD.
SSD is worthy if you are going to use your Ubuntu for business productive environments. The reason is that they are efficient but cost a bit more than the rotating HDDs.
10. Shift to a Lighter Desktop Environment
Ubuntu and all its derivatives support the installation of the desktop environments of your choice. If you have to use the original Ubuntu installation, then you can switch by installing a different desktop like Deepin.
Other desktop environments like XFCE, LXDE, Mate, KDE, etc come by default by the various variants of Ubuntu like Xubuntu, Lubuntu, Ubuntu Mate, etc.
XFCE and LXDE are really light, and they can ease the workload on memory when you are using your Ubuntu laptop. Installation of a different desktop environment on Ubuntu is easy. For instance, to install LXDE, type
sudo apt install lubuntu-desktop
The LXDE interface will install alongside some of its basic apps. You may, however, end up having more programs than you need. For instance, it will come with a file manager, text editor, and other software meant for the lite environment.
11. Clean Your Computer
Sometimes the cause of system crashes, failures, heating, and shutdown on your laptop is dust. How long have you used your laptop? (Mine is now 10 years old, and 7 years since I acquired it).
Yes, there is a lot of dust in my machine because I have never cleaned it. And the keyboard also broke, and I had to take it out – giving more space for dust to accumulate.
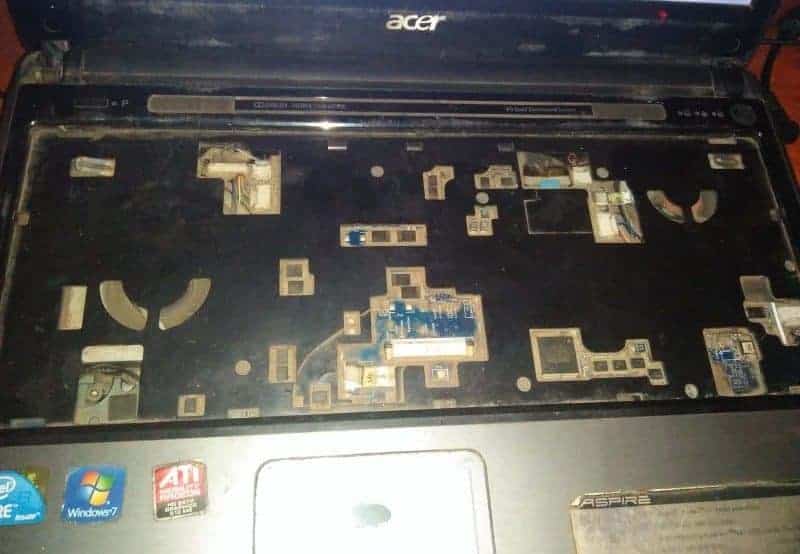

Whenever I am using Ubuntu, the laptop overheats, and that is especially true if I am playing videos. If you experience overheating on your laptop, you may want to take it for cleaning. (I will take mine when buying a new chassis with the missing keyboard. But don’t mind it, I have another one that is portable.)
Summary
Your laptop can slow down when you overwork it, or it cannot read information faster from the drives. Preventing it from system failures and boosting the memory will help you accomplish your tasks faster. Replacing dead drives and installing more RAM will boost your laptop performance.
Increasing the Swap space will help in relieving the RAM of your computer, and cleaning it will help the machine to cool down. With too much dust on the motherboard, it will be difficult to keep your machine cool even when the fans are running full speed. Leave a comment below and let us know how you make your laptop perform faster.





I have been through the whole content of this blog which is very informative and knowledgeable stuff